Google Sparrow and Bard are two different AI-powered initiatives by Google that showcase the potential of AI in enhancing human creativity and personalizing search results.
When comparing Google Sparrow and Bard; they are AI chatbots powered by different versions of Google’s Language Model for Dialogue Applications. They differ in their capabilities, features and goals.
You can find everything about Google Sparrow and Bard in this article.
Additionally, you can find how Google Sparrow differs from Bard models and how to choose one.
Google Sparrow Vs. Bard: Similarities And Differences
New advances in AI chatbots are happening quickly and are often being reported in the news.
Google Bard and Sparrow are two AI chatbots that are powered by different versions of Google’s Language Model for Dialogue Applications (LaMDA), a large language model (LLM) that can generate natural and fluent responses to any kind of prompt.
They have some similarities in their features and goals but also some differences.
What Is Google Sparrow?
Sparrow is an AI chatbot developed by Google subsidiary DeepMind that uses advanced Natural Language Processing(NLP) techniques.
It is based on the GPT-3 model designed to analyze the received text from the users and generate the responses.
Sparrow was introduced in September 2022 in a paper; regardless, it is in the research phase and has not been released publicly.
DeepMind CEO Demis Hassabis says a private beta version of Sparrow will be released in 2023.
Moreover, it can learn and draw information from Google searches. Besides, this model pays attention to accuracy, safety and practicality. Sparrow is developed by Google subsidiary DeepMind that uses advanced Natural Language Processing(NLP).
Unlike other chatbots that have gained popularity, Sparrow hasn’t been able to generate as much buzz due to the absence of a public API with it.
It is a research project to showcase the potential of an advanced language model for chatbots.
How Does Google Sparrow Work?
Sparrow is designed to talk with users, answer queries and search for information using Google.
The training model in Sparrow is similar to that of ChatGPT.
Meanwhile, it follows RLHF (Reinforcement learning from Human Feedback) protocols and large language models.
The working model of Google Sparrow is described below;
1. Pre-Training Language Models
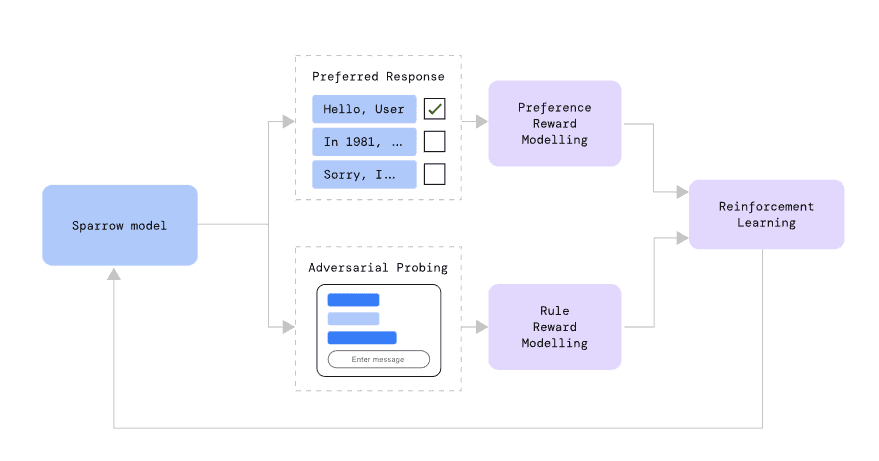
RLHF is based on people’s feedback which is used to train Sparrow.
Deepmind has set rules for Sparrow, such as not making threatening statements and hateful comments to make the model safe.
Additionally, Sparrow is trained with a rule model to indicate when it breaks the rules. This is done by asking participants to try and trick Sparrow.
This model shows answers with or without evidence retrieved from the internet and also determines when the answer should be supported with the evidence.
Sparrow presents four possible answers without supporting evidence when prompted with a query and initiates two Google search queries that could potentially yield two relevant results.
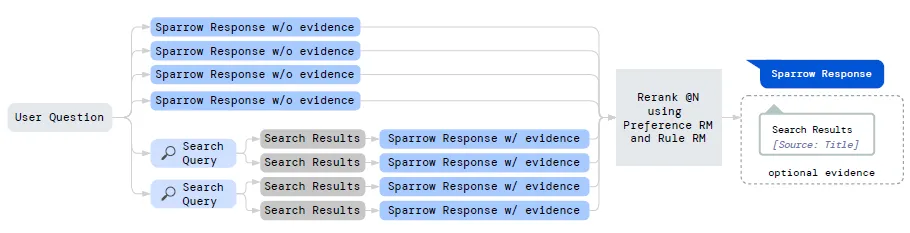
2. Reward Model Training
For each search, these results are conditionally sampled.
All results are scored by a Preference Reward and Rule Reward models, and the highest-scored result is shown to the users.
According to the participants, Sparrow’s answers are credible and support 78% of the evidence of the time.
Despite its capabilities, Sparrow is not immune to being fooled or tricked by participants, indicating that there is still room for improvement in its design and functionality.
What Is Google Bard?
Google Bard is a conversational AI service powered by LaMDA (Language Model for Dialogue Applications) that aims to build advanced analytics to produce information.
Its main goal is to retrieve information simply, like a digital assistant.
Moreover, it provides human-like conversational responses and generates and edits text.
Bard can access Google’s search engine. It is more likely to compete with Microsoft’s new AI Bing Chat, which can access the entire web.
However, you cannot see the citations footnote with the information links.
Read more to learn how to use Microsoft’s new AI Bing Chat.
How Does Google Bard Work?
Google Bard can only handle U.S. English language. Bard’s response addresses NORA questions which means No One Right Answer.
Here is how the Google Bard model works;
1. Flow Of Information
Bard provides the Knowledge Graph Card in the search when making queries that have simple answers, such as word definitions or overviews about a person or place.
Moreover, you can help the Bard chatbot by using the thumbs-up or thumbs-down buttons.
You can even regenerate the answers, just like in ChatGPT. Alternatively, you can click the Google It button for a regular search.
Bard chatbot also have a drafts option that allows you to select from the different answer in bullet format. A Reset chat button exists to terminate and start a new chat session.
Further, you can access the Bard Activity, which allows seeing the history of your searches.
There is not much documentation about how Google has refined the technology for use in Bard; however, you can find documentation on how large language model works.
2. Training Data Set
Bard first uses the LaMDA language model to understand the queries and then draws the information it finds across the web to form a conversational reply.
It uses a type of neural network called a Transformer to understand and generate human-like language.
Training data works by enabling LaMDA to learn from a large amount of data enabling it to achieve objectives, quality and safety.
3. Pre-Training
In the pre-training process, LaMDA is trained on a large dataset of 1.56 trillion words from public dialog data and public web documents.
This dataset covers a wide range of topics and domains. It also helps LaMDA learn general knowledge and skills.
4. Fine Training
LaMDA is trained to perform generative and classification tasks in the fine-tuning process.
Generative tasks produce natural language responses to give contexts, while classification tasks predict each response’s safety and quality.
In this way, LaMDA learns how to generate responses and avoid inappropriate responses.

Comparatively, Bard provides high-quality and accurate responses to the user’s queries.
How To Join Google Bard Waitlists?
Bard is now available only in the U.S. and U.K. If you reside in a country where Google Bard is available, you must pass the waitlist to access it.
You can sign up for the waitlist with these instructions.
- First, visit the Google Bard homepage, and you will be directed to the landing page.
- Then, click on the Join Waitlist button to get started. Sign in to your personal Google account if needed.
- Finally, select Yes, I’m in to join the waitlist. You will get an email notification when you get access to Bard.

If Bard is not supported in your region, you can still access it by using VPN.
Note: Users cannot access Bard with Google Workspace accounts, so use your personal Google account.
Google Sparrow Vs. Bard: Similarities
Google Sparrow will be learning from responses just like Bard. Some of the similarities between them are:
1. Architecture And Development
Sparrow and Google Bard are AI chatbots based on the Transformer architecture, a neural network that can learn from large text data and predict the next words in a sequence.
However, they use different versions of Google’s Language Model for Dialogue Applications.
2. Large Language Model
Sparrow and Google Bard use large language models (LLMs) to generate natural and fluent responses to any prompt.
LLMs are a kind of AI technology that learns by analyzing vast amounts of text data from various sources on the web.
Furthermore, they both draw on information from the web to provide accurate answers when possible.
3. Pre-Training With Data
Google Sparrow and Bard are pre-trained on a large corpus of text data. Besides, they both use information from the web to provide high-quality responses.
Yet, they face similar challenges and limitations, such as biases, inaccuracies, and ethical concerns.
4. Large Parameter Sizes
The exact number of parameters of Sparrow and Google Bard is not publicly available.
However, some sources say Google Bard may have up to 2 billion parameters.
Similarly, Sparrow uses a modified version of LaMDA, which may have more parameters than Bard.
Read on to learn the similarities and differences between Google Bard and ChatGPT.
Google Sparrow Vs. Bard: Major Differences
Sparrow and Bard differ from one another in the way they collect data and learn.
They both are AI chatbots powered by different versions of Google’s LaMDA.
However, they differ in their capabilities, features and goals.
| Google Sparrow | Google Bard |
|---|---|
| It is a project by DeepMind aims to create a safer and reliable dialogue agent. | It is an experiment by Google that lets users experience a chat interface. |
| Powered by Transformer, a neural network architecture. | Powered by a lightweight version of LaMDA. |
| Can answer questions but it will cite sources for its answer. | Can answer question,generate content and suggest queries for Google Search. |
| Learn and draw information from Google’s searches. | Can generate responses based on web information. |
| Designed to be more helpful, correct and harmless. | designed to combine breadth of the World’s knowledge with the power, intelligence. |
| Introduced as a proof of concept in research paper but is has not been released to public yet. | Available in UK and USA but still not available widely. |
Now, let’s look into the differences between these two platforms in detail.
1. Mission And Reach
The mission of Google Sparrow and Bard is to provide AI-powered conversation using LLM.
They both aim to help people with various tasks such as boosting, accelerating, explaining concepts and providing personalized assistance.
However, they both are still in the experimental phase. Bard is currently open for limited users in U.S. and UK, while Sparrow is still in the research stage.
2. Learning/Training Data
Google Sparrow and Bard are trained on large web text and dialog data sets, while the exact sources of their training data are not disclosed by Google publicly.
Google Bard is powered by a lightweight version of LaMDA, where its LLM was pre-trained on 1.56 trillion words.
The Infiniset consists of 12.5% C4-based data, 12.55 English language Wikipedia, 12.5% code documents, tutorials, 6.25% English web documents, 6.25% Non-English web documents and 50% dialog data from public forums.
Whereas Google Sparrow is based on a new LLM that DeepMind is developing.
However, the detail of this LLM is not revealed yet. DeepMind has been working on various LLMs, such as Gopher and switch models.
3. Deployment And Purpose
Google Bard is designed as a complementary experience to Google Search, which allows you to check its responses or explore sources across the web.
Regardless, Sparrow is imagined as a more independent, personalized assistant that can learn from your interests and priorities.
The Bottom Line
Google Sparrow and Bard represent two different approaches to conversational AI, each with its own strengths and weaknesses.
As these chatbots evolve and improve, they may offer new possibilities and challenges for users and developers.
AI-powered conversational interfaces can predictably lead to further innovations and improvements.
Hopefully, this article helps you learn more about Google Sparrow and Bard.
Continue reading to find out how to access Google Bard and use Google Bard properly.








3 thoughts on “Google Sparrow Vs. Bard: A Comprehensive Analysis”